3900. Find Weighted Median Node In Tree¶
3900. Find Weighted Median Node in Tree
Hard
You are given an integer n and an undirected, weighted tree rooted at node 0 with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. This is represented by a 2D array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates an edge from node ui to vi with weight wi.
The weighted median node is defined as the first node x on the path from ui to vi such that the sum of edge weights from ui to x is greater than or equal to half of the total path weight.
You are given a 2D integer array queries. For each queries[j] = [uj, vj], determine the weighted median node along the path from uj to vj.
Return an array ans, where ans[j] is the node index of the weighted median for queries[j].
Example 1:
Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1,7]], queries = [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: [0,1]
Explanation:
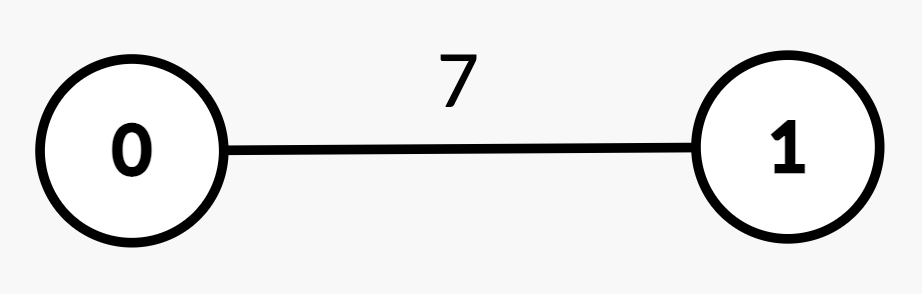
| Query | Path | Edge Weights | Total Path Weight | Half | Explanation | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1, 0] | 1 → 0 | [7] | 7 | 3.5 | Sum from 1 → 0 = 7 >= 3.5, median is node 0. | 0 |
[0, 1] | 0 → 1 | [7] | 7 | 3.5 | Sum from 0 → 1 = 7 >= 3.5, median is node 1. | 1 |
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,2],[2,0,4]], queries = [[0,1],[2,0],[1,2]]
Output: [1,0,2]
Explanation:
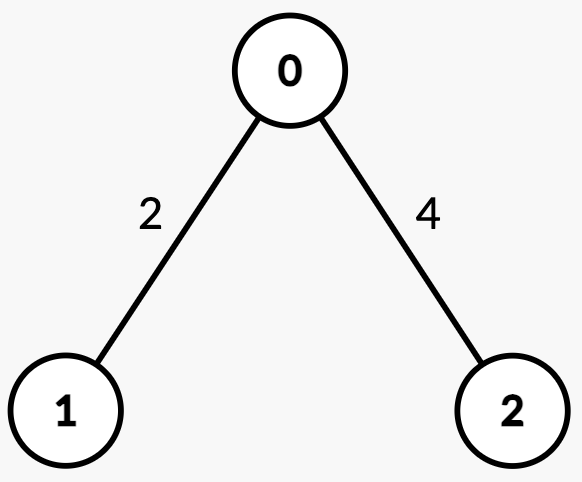
| Query | Path | Edge Weights | Total Path Weight | Half | Explanation | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[0, 1] | 0 → 1 | [2] | 2 | 1 | Sum from 0 → 1 = 2 >= 1, median is node 1. | 1 |
[2, 0] | 2 → 0 | [4] | 4 | 2 | Sum from 2 → 0 = 4 >= 2, median is node 0. | 0 |
[1, 2] | 1 → 0 → 2 | [2, 4] | 6 | 3 | Sum from 1 → 0 = 2 < 3.Sum from 1 → 2 = 2 + 4 = 6 >= 3, median is node 2. | 2 |
Example 3:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,2,5],[1,3,1],[2,4,3]], queries = [[3,4],[1,2]]
Output: [2,2]
Explanation:
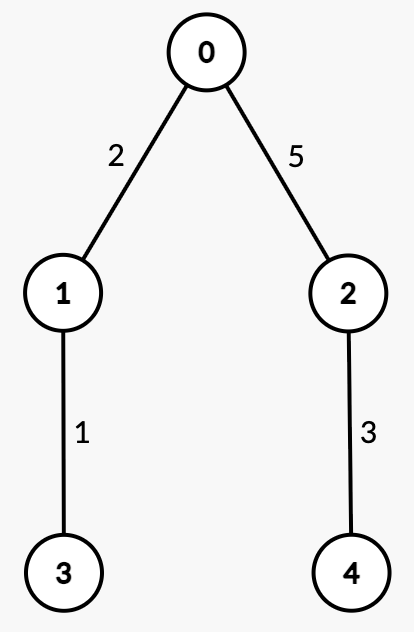
| Query | Path | Edge Weights | Total Path Weight | Half | Explanation | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[3, 4] | 3 → 1 → 0 → 2 → 4 | [1, 2, 5, 3] | 11 | 5.5 | Sum from 3 → 1 = 1 < 5.5.Sum from 3 → 0 = 1 + 2 = 3 < 5.5.Sum from 3 → 2 = 1 + 2 + 5 = 8 >= 5.5, median is node 2. | 2 |
[1, 2] | 1 → 0 → 2 | [2, 5] | 7 | 3.5 | Sum from | 2 |
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i] == [ui, vi, wi]0 <= ui, vi < n1 <= wi <= 1091 <= queries.length <= 105queries[j] == [uj, vj]0 <= uj, vj < n- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution¶
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
static class Pair {
int node;
long weight;
public Pair(int node, long weight) {
this.node = node;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + node + " " + weight + ")";
}
}
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Pair >> adj;
private long pref[];
private int dp[][];
private int depth[];
public int[] findMedian(int n, int[][] edges, int[][] queries) {
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
u++;
v++;
adj.get(u).add(new Pair(v, w * 1L));
adj.get(v).add(new Pair(u, w * 1L));
}
Build_pref(n);
dp = new int[n + 1][19];
depth = new int[n + 1];
dfs(1, 0);
int res[] = new int[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
int u = queries[i][0] + 1, v = queries[i][1] + 1;
if (u == v) {
res[i] = u - 1;
continue;
}
int lca = lca(u, v);
long total_sum = pref[u] + pref[v] - 2 * pref[lca];
/* u, . , . , lca, . . . , v */
/* first check from u to lca if there exist some node */
/* next check from lca to v */
int check_left = check_left(u, lca, total_sum);
if (check_left != -1)
res[i] = check_left - 1;
else
res[i] = check_right(v, lca, total_sum, pref[u] - pref[lca]) - 1;
}
return res;
}
private int check_left(int u, int lca, long total) {
int low = 0, high = depth[u] - depth[lca], ans = -1;
double req = (double)(total * 1.0 / 2 * 1.0);
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
long sum = pref[u] - pref[find_kth_parent(u, mid)];
if (sum >= req) {
ans = find_kth_parent(u, mid);
high = mid - 1;
} else
low = mid + 1;
}
return ans;
}
private int check_right(int v, int lca, long total, long prev_sum) {
int low = 0, high = depth[v] - depth[lca], ans = -1;
double req = (double)(total * 1.0 / 2 * 1.0);
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
long sum = prev_sum + pref[find_kth_parent(v, mid)] - pref[lca];
if (sum >= req) {
ans = find_kth_parent(v, mid);
low = mid + 1;
} else
high = mid - 1;
}
return ans;
}
private int lca(int u, int v) {
if (depth[u] > depth[v]) {
int temp = u;
u = v;
v = temp;
}
int diff = depth[v] - depth[u];
v = find_kth_parent(v, diff);
if (u == v)
return u;
for (int i = 18; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dp[u][i] != dp[v][i]) {
u = dp[u][i];
v = dp[v][i];
}
}
return dp[u][0];
}
private int find_kth_parent(int u, int k) {
int count = 0;
while (k > 0) {
if (k % 2 == 1)
u = dp[u][count];
count++;
k >>= 1;
}
return u;
}
private void dfs(int u, int par) {
dp[u][0] = par;
for (int i = 1; i <= 18; i++)
dp[u][i] = dp[dp[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.get(u).size(); i++) {
int v = adj.get(u).get(i).node;
if (v != par) {
depth[v] = 1 + depth[u];
dfs(v, u);
}
}
}
private void Build_pref(int n) {
pref = new long[n + 1];
int vis[] = new int[n + 1];
pref[1] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(1);
vis[1] = 1;
while (q.size() > 0) {
int curr_node = q.peek();
q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < adj.get(curr_node).size(); i++) {
int child_node = adj.get(curr_node).get(i).node;
long child_dist = adj.get(curr_node).get(i).weight;
if (vis[child_node] == 0) {
vis[child_node] = 1;
pref[child_node] = pref[curr_node] + child_dist;
q.offer(child_node);
}
}
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity: O(?)
- Space Complexity: O(?)
Explanation¶
[Add detailed explanation here]