3853. Minimum Weighted Subgraph With The Required Paths Ii¶
Difficulty: Hard
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
3853. Minimum Weighted Subgraph With the Required Paths II
Hard
You are given an undirected weighted tree with n nodes, numbered from 0 to n - 1. It is represented by a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi with weight wi.
Additionally, you are given a 2D integer array queries, where queries[j] = [src1j, src2j, destj].
Return an array answer of length equal to queries.length, where answer[j] is the minimum total weight of a subtree such that it is possible to reach destj from both src1j and src2j using edges in this subtree.
A subtree here is any connected subset of nodes and edges of the original tree forming a valid tree.
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,5],[1,4,4],[2,5,6]], queries = [[2,3,4],[0,2,5]]
Output: [12,11]
Explanation:
The blue edges represent one of the subtrees that yield the optimal answer.
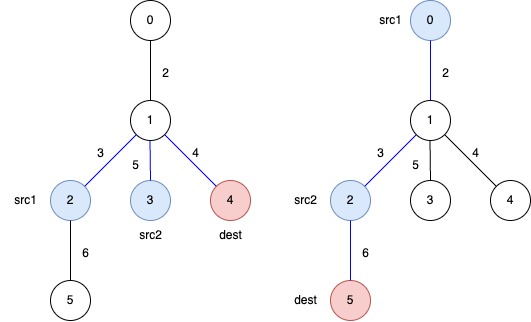
-
answer[0]: The total weight of the selected subtree that ensures a path fromsrc1 = 2andsrc2 = 3todest = 4is3 + 5 + 4 = 12. -
answer[1]: The total weight of the selected subtree that ensures a path fromsrc1 = 0andsrc2 = 2todest = 5is2 + 3 + 6 = 11.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[1,0,8],[0,2,7]], queries = [[0,1,2]]
Output: [15]
Explanation:
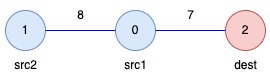
answer[0]: The total weight of the selected subtree that ensures a path fromsrc1 = 0andsrc2 = 1todest = 2is8 + 7 = 15.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi < n1 <= wi <= 1041 <= queries.length <= 105queries[j].length == 30 <= src1j, src2j, destj < nsrc1j,src2j, anddestjare pairwise distinct.- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution¶
class Solution {
static class Pair {
int node, weight;
public Pair(int node, int weight) {
this.node = node;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + node + " " + weight + ")";
}
}
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Pair>> adj;
private int dp[][];
private int depth[];
private int vis[];
private int pref[];
private int res[];
public int[] minimumWeight(int[][] edges, int[][] queries) {
int n = edges.length + 1;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int edge[] : edges) {
int u = edge[0] + 1, v = edge[1] + 1, wt = edge[2];
adj.get(u).add(new Pair(v, wt));
adj.get(v).add(new Pair(u, wt));
}
dp = new int[n + 1][19];
depth = new int[n + 1];
vis = new int[n + 1];
dfs(1, 0);
pref = new int[n + 1];
build_pref(n);
res = new int[queries.length];
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(pref));
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
int src1 = queries[i][0] + 1, src2 = queries[i][1] + 1, dest = queries[i][2] + 1;
int lca1 = lca(src1, dest), lca2 = lca(src2, dest), lca3 = lca(src1, src2);
int dist1 = pref[src1] + pref[dest] - 2 * pref[lca1];
int dist2 = pref[src2] + pref[dest] - 2 * pref[lca2];
int dist3 = pref[src1] + pref[src2] - 2 * pref[lca3];
res[i] = (dist1 + dist2 + dist3) / 2;
}
return res;
}
private void build_pref(int n) {
pref[1] = 0;
vis = new int[n + 1];
vis[1] = 1;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(1);
while (q.size() > 0) {
int curr_node = q.peek();
int curr_dist = pref[curr_node];
q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < adj.get(curr_node).size(); i++) {
int child_node = adj.get(curr_node).get(i).node;
int child_weight = adj.get(curr_node).get(i).weight;
if (vis[child_node] == 0) {
vis[child_node] = 1;
pref[child_node] = child_weight + curr_dist;
q.offer(child_node);
}
}
}
}
private int find_kth_parent(int u, int k) {
int count = 0;
while (k > 0) {
if (k % 2 == 1) u = dp[u][count];
count++;
k >>= 1;
}
return u;
}
private int lca(int u, int v) {
if (depth[u] > depth[v]) {
int temp = u;
u = v;
v = temp;
}
int diff = depth[v] - depth[u];
v = find_kth_parent(v, diff);
if (u == v) return u;
for (int i = 18; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dp[u][i] != dp[v][i]) {
u = dp[u][i];
v = dp[v][i];
}
}
return dp[u][0];
}
private void dfs(int u, int par) {
vis[u] = 1;
dp[u][0] = par;
for (int i = 1; i < 19; i++) dp[u][i] = dp[dp[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.get(u).size(); i++) {
int v = adj.get(u).get(i).node;
if (vis[v] == 0) {
depth[v] = 1 + depth[u];
dfs(v, u);
}
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here