3729. Unit Conversion I¶
3729. Unit Conversion I
Medium
There are n types of units indexed from 0 to n - 1. You are given a 2D integer array conversions of length n - 1, where conversions[i] = [sourceUniti, targetUniti, conversionFactori]. This indicates that a single unit of type sourceUniti is equivalent to conversionFactori units of type targetUniti.
Return an array baseUnitConversion of length n, where baseUnitConversion[i] is the number of units of type i equivalent to a single unit of type 0. Since the answer may be large, return each baseUnitConversion[i] modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
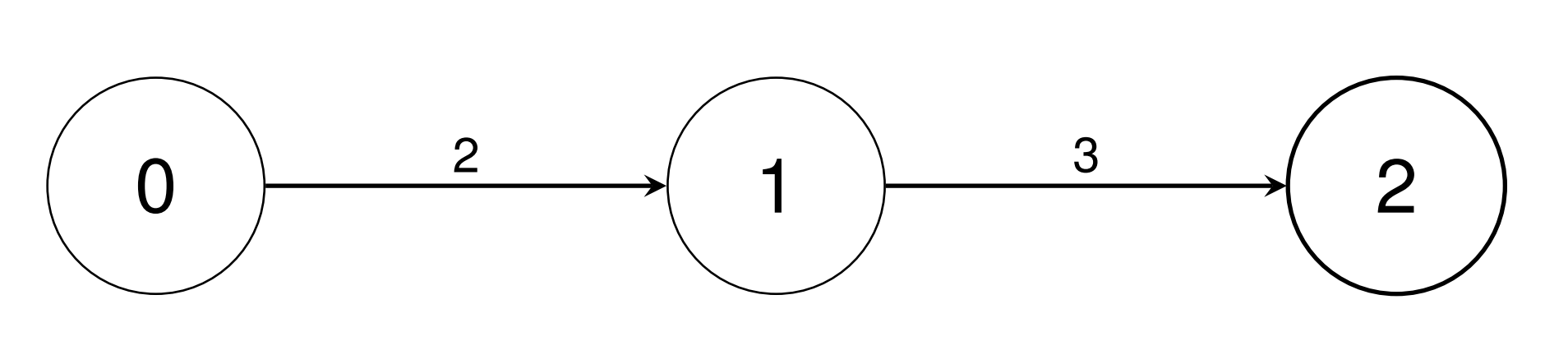
Input: conversions = [[0,1,2],[1,2,3]]
Output: [1,2,6]
Explanation:
- Convert a single unit of type 0 into 2 units of type 1 using
conversions[0]. - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 6 units of type 2 using
conversions[0], thenconversions[1].
Example 2:
Input: conversions = [[0,1,2],[0,2,3],[1,3,4],[1,4,5],[2,5,2],[4,6,3],[5,7,4]]
Output: [1,2,3,8,10,6,30,24]
Explanation:
- Convert a single unit of type 0 into 2 units of type 1 using
conversions[0]. - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 3 units of type 2 using
conversions[1]. - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 8 units of type 3 using
conversions[0], thenconversions[2]. - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 10 units of type 4 using
conversions[0], thenconversions[3]. - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 6 units of type 5 using
conversions[1], thenconversions[4]. - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 30 units of type 6 using
conversions[0],conversions[3], thenconversions[5]. - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 24 units of type 7 using
conversions[1],conversions[4], thenconversions[6].
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105conversions.length == n - 10 <= sourceUniti, targetUniti < n1 <= conversionFactori <= 109- It is guaranteed that unit 0 can be converted into any other unit through a unique combination of conversions without using any conversions in the opposite direction.
Solution¶
class Solution {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Pair>> adj;
private long mod = (long)(1e9 + 7);
static class Pair {
int node;
long dist;
public Pair(int node, long dist) {
this.node = node;
this.dist = dist;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + node + " " + dist + ")";
}
}
static class custom_sort implements Comparator<Pair> {
@Override
public int compare(Pair first, Pair second) {
return Long.compare(first.dist, second.dist);
}
}
public int[] baseUnitConversions(int[][] conversions) {
int n = conversions.length;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int current[] : conversions) {
int u = current[0], v = current[1], wt = current[2];
adj.get(u).add(new Pair(v, wt));
adj.get(v).add(new Pair(u, wt));
}
PriorityQueue<Pair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new custom_sort());
long dp[] = new long[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, (long)(2e19));
dp[0] = 1;
pq.offer(new Pair(0, 1));
while (pq.size() > 0) {
int curr_node = pq.peek().node;
long curr_dist = pq.peek().dist;
pq.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < adj.get(curr_node).size(); i++) {
int child_node = adj.get(curr_node).get(i).node;
long child_dist = adj.get(curr_node).get(i).dist;
if (dp[child_node] > (curr_dist * 1L * child_dist)) {
dp[child_node] = (int)((curr_dist * 1L * child_dist) % mod);
pq.offer(new Pair(child_node, dp[child_node]));
}
}
}
int res[] = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) res[i] = (int)(dp[i]);
return res;
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity: O(?)
- Space Complexity: O(?)
Explanation¶
[Add detailed explanation here]