3603. Check If Dfs Strings Are Palindromes¶
3603. Check if DFS Strings Are Palindromes
Hard
You are given a tree rooted at node 0, consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented by an array parent of size n, where parent[i] is the parent of node i. Since node 0 is the root, parent[0] == -1.
You are also given a string s of length n, where s[i] is the character assigned to node i.
Consider an empty string dfsStr, and define a recursive function dfs(int x) that takes a node x as a parameter and performs the following steps in order:
- Iterate over each child
yofxin increasing order of their numbers, and calldfs(y). - Add the character
s[x]to the end of the stringdfsStr.
Note that dfsStr is shared across all recursive calls of dfs.
You need to find a boolean array answer of size n, where for each index i from 0 to n - 1, you do the following:
- Empty the string
dfsStrand calldfs(i). - If the resulting string
dfsStris a palindrome, then setanswer[i]totrue. Otherwise, setanswer[i]tofalse.
Return the array answer.
A palindrome is a string that reads the same forward and backward.
Example 1:
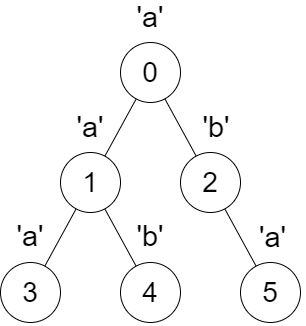
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,2], s = "aababa"
Output: [true,true,false,true,true,true]
Explanation:
- Calling
dfs(0)results in the stringdfsStr = "abaaba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(1)results in the stringdfsStr = "aba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(2)results in the stringdfsStr = "ab", which is not a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(3)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(4)results in the stringdfsStr = "b", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(5)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome.
Example 2:
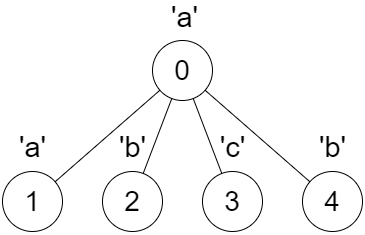
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,0,0], s = "aabcb"
Output: [true,true,true,true,true]
Explanation:
Every call on dfs(x) results in a palindrome string.
Constraints:
n == parent.length == s.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= parent[i] <= n - 1for alli >= 1.parent[0] == -1parentrepresents a valid tree.sconsists only of lowercase English letters.
Solution¶
class Solution {
private long base = 911;
private long mod = 1000000007L;
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj;
private long forwardHash[];
private long reverseHash[];
private int len[];
private long pow[];
public boolean[] findAnswer(int[] parent, String s) {
int n = parent.length;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(parent[i] != -1){
adj.get(parent[i]).add(i);
}
}
for (ArrayList<Integer> curr : adj) Collections.sort(curr);
pow = new long[n + 1];
forwardHash = new long[n];
reverseHash = new long[n];
len = new int[n];
pow[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) pow[i] = (pow[i - 1] * base) % mod;
dfs(0, s);
boolean[] answer = new boolean[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (forwardHash[i] == reverseHash[i]) answer[i] = true;
else answer[i] = false;
}
return answer;
}
public void dfs(int u, String s) {
len[u] = 1;
forwardHash[u] = 0;
for(int v : adj.get(u)) {
dfs(v, s);
forwardHash[u] = (forwardHash[u] * pow[len[v]] + forwardHash[v]) % mod;
len[u] += len[v];
}
forwardHash[u] = (forwardHash[u] * base + (s.charAt(u) - 'a' + 1)) % mod;
reverseHash[u] = (s.charAt(u) - 'a' + 1);
for (int i = adj.get(u).size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int v = adj.get(u).get(i);
reverseHash[u] = (reverseHash[u] * pow[len[v]] + reverseHash[v]) % mod;
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity: O(?)
- Space Complexity: O(?)
Explanation¶
[Add detailed explanation here]