2545. Height Of Binary Tree After Subtree Removal Queries¶
Difficulty: Hard
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
2545. Height of Binary Tree After Subtree Removal Queries
Hard
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is assigned a unique value from 1 to n. You are also given an array queries of size m.
You have to perform m independent queries on the tree where in the ith query you do the following:
- Remove the subtree rooted at the node with the value
queries[i]from the tree. It is guaranteed thatqueries[i]will not be equal to the value of the root.
Return an array answer of size m where answer[i] is the height of the tree after performing the ith query.
Note:
- The queries are independent, so the tree returns to its initial state after each query.
- The height of a tree is the number of edges in the longest simple path from the root to some node in the tree.
Example 1:
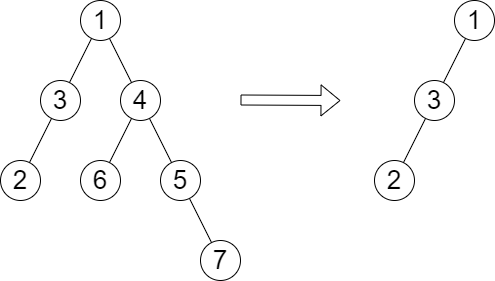
Input: root = [1,3,4,2,null,6,5,null,null,null,null,null,7], queries = [4] Output: [2] Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree after removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree is 2 (The path 1 -> 3 -> 2).
Example 2:
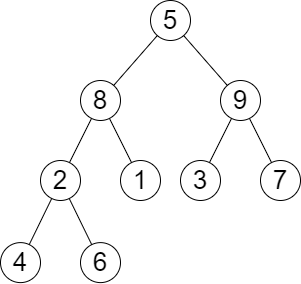
Input: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], queries = [3,2,4,8] Output: [3,2,3,2] Explanation: We have the following queries: - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 3. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 4). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 2. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 1). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 6). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 8. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 9 -> 3).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
m == queries.length1 <= m <= min(n, 104)1 <= queries[i] <= nqueries[i] != root.val
Solution¶
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj;
private int depth[];
private ArrayList<Integer> tour;
private int first[];
private int last[];
public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {
Build_Graph(root);
depth = new int[(int)(1e5 + 1)];
tour = new ArrayList<>();
first = new int[(int)(1e5 + 1)];
last = new int[(int)(1e5 + 1)];
Arrays.fill(first, -1); Arrays.fill(last, -1);
Euler_Dfs(root.val, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < tour.size(); i++) {
if (first[tour.get(i)] == -1) first[tour.get(i)] = i;
else last[tour.get(i)] = i;
}
int maxi_pref[] = new int[tour.size() + 1];
int maxi_suff[] = new int[tour.size() + 1];
int maxi = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tour.size(); i++) {
int current = depth[tour.get(i)];
maxi = Math.max(maxi, current);
maxi_pref[i] = maxi;
}
maxi = 0;
for (int i = tour.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int current = depth[tour.get(i)];
maxi = Math.max(maxi, current);
maxi_suff[i] = maxi;
}
int res[] = new int[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
int node = queries[i];
int left = first[node];
int right = last[node];
int current_maxi = 0;
if (left - 1 >= 0) current_maxi = Math.max(current_maxi, maxi_pref[left - 1]);
if (right + 1 < tour.size()) current_maxi = Math.max(current_maxi, maxi_suff[right + 1]);
res[i] = current_maxi;
}
return res;
}
private void Euler_Dfs(int u , int par) {
tour.add(u);
for (int v : adj.get(u)) {
if (v != par) {
depth[v] = 1 + depth[u];
Euler_Dfs(v, u);
}
}
tour.add(u);
}
private void Build_Graph(TreeNode root) {
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= (int)(1e5 + 1); i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (q.size() > 0) {
int len = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int u = q.peek().val;
if (q.peek().left != null) {
q.offer(q.peek().left);
int v = q.peek().left.val;
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
if (q.peek().right != null) {
q.offer(q.peek().right);
int v = q.peek().right.val;
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
q.poll();
}
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here