2162. Partition Array Into Two Arrays To Minimize Sum Difference¶
Difficulty: Hard
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
2162. Partition Array Into Two Arrays to Minimize Sum Difference
Hard
You are given an integer array nums of 2 * n integers. You need to partition nums into two arrays of length n to minimize the absolute difference of the sums of the arrays. To partition nums, put each element of nums into one of the two arrays.
Return the minimum possible absolute difference.
Example 1:
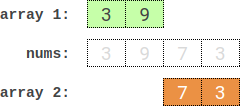
Input: nums = [3,9,7,3] Output: 2 Explanation: One optimal partition is: [3,9] and [7,3]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((3 + 9) - (7 + 3)) = 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-36,36] Output: 72 Explanation: One optimal partition is: [-36] and [36]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((-36) - (36)) = 72.
Example 3:
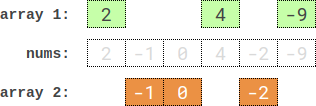
Input: nums = [2,-1,0,4,-2,-9] Output: 0 Explanation: One optimal partition is: [2,4,-9] and [-1,0,-2]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((2 + 4 + -9) - (-1 + 0 + -2)) = 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 15nums.length == 2 * n-107 <= nums[i] <= 107
Solution¶
class Solution {
private HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> firstMap;
private HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> secondMap;
public int minimumDifference(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
firstMap = new HashMap<>();
secondMap = new HashMap<>();
int[] first = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, n / 2);
int[] second = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, n / 2, n);
build(0, first, 0, 0, 1);
build(0, second, 0, 0, 2);
int total = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
int mini = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i <= n / 2; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> leftSums = firstMap.getOrDefault(i, new ArrayList<>());
ArrayList<Integer> rightSums = secondMap.getOrDefault(n / 2 - i, new ArrayList<>());
Collections.sort(rightSums);
for (int ele1 : leftSums) {
int target = total / 2 - ele1;
int idx = Collections.binarySearch(rightSums, target);
if (idx < 0) idx = -idx - 1;
if (idx < rightSums.size()) {
int currentSum = ele1 + rightSums.get(idx);
int rem = total - currentSum;
mini = Math.min(mini, Math.abs(currentSum - rem));
}
if (idx > 0) {
int currentSum = ele1 + rightSums.get(idx - 1);
int rem = total - currentSum;
mini = Math.min(mini, Math.abs(currentSum - rem));
}
}
}
return mini;
}
private void build(int ind, int[] arr, int count, int sum, int id) {
if (ind == arr.length) {
if (id == 1)
firstMap.computeIfAbsent(count, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(sum);
else
secondMap.computeIfAbsent(count, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(sum);
return;
}
build(ind + 1, arr, count + 1, sum + arr[ind], id);
build(ind + 1, arr, count, sum, id);
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here