2104. Operations On Tree¶
Difficulty: Medium
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
2104. Operations on Tree
Medium
You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 in the form of a parent array parent where parent[i] is the parent of the ith node. The root of the tree is node 0, so parent[0] = -1 since it has no parent. You want to design a data structure that allows users to lock, unlock, and upgrade nodes in the tree.
The data structure should support the following functions:
- Lock: Locks the given node for the given user and prevents other users from locking the same node. You may only lock a node using this function if the node is unlocked.
- Unlock: Unlocks the given node for the given user. You may only unlock a node using this function if it is currently locked by the same user.
- Upgrade: Locks the given node for the given user and unlocks all of its descendants regardless of who locked it. You may only upgrade a node if all 3 conditions are true:
- The node is unlocked,
- It has at least one locked descendant (by any user), and
- It does not have any locked ancestors.
Implement the LockingTree class:
LockingTree(int[] parent)initializes the data structure with the parent array.lock(int num, int user)returnstrueif it is possible for the user with iduserto lock the nodenum, orfalseotherwise. If it is possible, the nodenumwill become locked by the user with iduser.unlock(int num, int user)returnstrueif it is possible for the user with iduserto unlock the nodenum, orfalseotherwise. If it is possible, the nodenumwill become unlocked.upgrade(int num, int user)returnstrueif it is possible for the user with iduserto upgrade the nodenum, orfalseotherwise. If it is possible, the nodenumwill be upgraded.
Example 1:
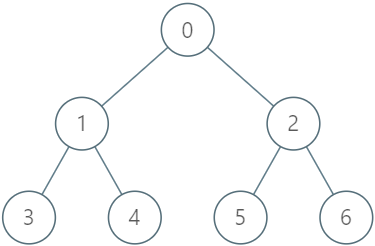
Input
["LockingTree", "lock", "unlock", "unlock", "lock", "upgrade", "lock"]
[[[-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [2, 2], [2, 3], [2, 2], [4, 5], [0, 1], [0, 1]]
Output
[null, true, false, true, true, true, false]
Explanation
LockingTree lockingTree = new LockingTree([-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
lockingTree.lock(2, 2); // return true because node 2 is unlocked.
// Node 2 will now be locked by user 2.
lockingTree.unlock(2, 3); // return false because user 3 cannot unlock a node locked by user 2.
lockingTree.unlock(2, 2); // return true because node 2 was previously locked by user 2.
// Node 2 will now be unlocked.
lockingTree.lock(4, 5); // return true because node 4 is unlocked.
// Node 4 will now be locked by user 5.
lockingTree.upgrade(0, 1); // return true because node 0 is unlocked and has at least one locked descendant (node 4).
// Node 0 will now be locked by user 1 and node 4 will now be unlocked.
lockingTree.lock(0, 1); // return false because node 0 is already locked.
Constraints:
n == parent.length2 <= n <= 20000 <= parent[i] <= n - 1fori != 0parent[0] == -10 <= num <= n - 11 <= user <= 104parentrepresents a valid tree.- At most
2000calls in total will be made tolock,unlock, andupgrade.
Solution¶
import java.util.*;
class LockingTree {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj;
private int par[];
private int map[];
public LockingTree(int[] parent) {
int n = parent.length;
par = new int[n + 1]; par[0] = -1;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
map = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(map, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int p = par[i] = parent[i];
adj.get(p).add(i);
}
}
public boolean lock(int num, int user) {
if (map[num] == -1) {
map[num] = user;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean unlock(int num, int user) {
if (map[num] == user) {
map[num] = -1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean upgrade(int num, int user) {
if (check(num, user)) {
doUpgrade(num, user);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private boolean check(int node, int user) {
if (map[node] != -1) return false;
int boolVal1[] = new int[1];
int boolVal2[] = new int[1];
checkDescendant(node, boolVal1);
checkAncestor(node, boolVal2);
return boolVal1[0] == 1 && boolVal2[0] == 1;
}
private void doUpgrade(int node, int user) {
map[node] = user;
unLockAll(node);
}
private void unLockAll(int node) {
for (int v : adj.get(node)) {
if (v != par[v]) {
map[v] = -1;
unLockAll(v);
}
}
}
private void checkDescendant(int node, int[] boolVal) {
for (int v : adj.get(node)) {
if (v != par[v]) {
if (map[v] != -1) {
boolVal[0] = 1;
return;
}
checkDescendant(v, boolVal);
}
}
}
private void checkAncestor(int node, int[] boolVal) {
node = par[node];
boolVal[0] = 1;
while (node != -1) {
if (map[node] != -1) {
boolVal[0] = 0;
return;
}
node = par[node];
}
}
}
/**
* Your LockingTree object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LockingTree obj = new LockingTree(parent);
* boolean param_1 = obj.lock(num,user);
* boolean param_2 = obj.unlock(num,user);
* boolean param_3 = obj.upgrade(num,user);
*/
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here