1716. Maximum Non Negative Product In A Matrix¶
Difficulty: Medium
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
1716. Maximum Non Negative Product in a Matrix
Medium
You are given a m x n matrix grid. Initially, you are located at the top-left corner (0, 0), and in each step, you can only move right or down in the matrix.
Among all possible paths starting from the top-left corner (0, 0) and ending in the bottom-right corner (m - 1, n - 1), find the path with the maximum non-negative product. The product of a path is the product of all integers in the grid cells visited along the path.
Return the maximum non-negative product modulo 109 + 7. If the maximum product is negative, return -1.
Notice that the modulo is performed after getting the maximum product.
Example 1:
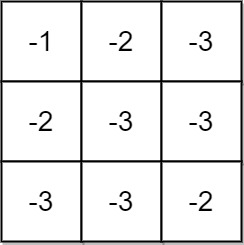
Input: grid = [[-1,-2,-3],[-2,-3,-3],[-3,-3,-2]] Output: -1 Explanation: It is not possible to get non-negative product in the path from (0, 0) to (2, 2), so return -1.
Example 2:
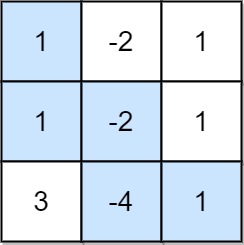
Input: grid = [[1,-2,1],[1,-2,1],[3,-4,1]] Output: 8 Explanation: Maximum non-negative product is shown (1 * 1 * -2 * -4 * 1 = 8).
Example 3:
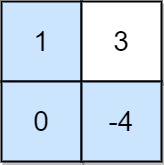
Input: grid = [[1,3],[0,-4]] Output: 0 Explanation: Maximum non-negative product is shown (1 * 0 * -4 = 0).
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 15-4 <= grid[i][j] <= 4
Solution¶
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
static class Tuple {
int row, col;
long val;
public Tuple(int row, int col, long val) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Tuple{" +
"row=" + row +
", col=" + col +
", val=" + val +
'}';
}
}
private int mod = (int)(1e9 + 7);
public int maxProductPath(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length, m = grid[0].length;
Queue<Tuple> q = new LinkedList<>();
int dir[][] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}};
long dp[][][] = new long[n + 1][m + 1][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dp[i][j][0] = Long.MIN_VALUE / 10;
dp[i][j][1] = Long.MAX_VALUE / 10;
}
}
dp[0][0][0] = grid[0][0];
dp[0][0][1] = grid[0][0];
q.offer(new Tuple(0, 0, grid[0][0]));
while (q.size() > 0) {
int currRow = q.peek().row, currCol = q.peek().col;
long currVal = q.peek().val;
q.poll();
for (int dire[] : dir) {
int newRow = currRow + dire[0], newCol = currCol + dire[1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < n && newCol >= 0 && newCol < m) {
long newVal = (currVal * 1L * grid[newRow][newCol]);
if (newVal < 0) {
if (dp[newRow][newCol][1] > newVal) {
dp[newRow][newCol][1] = newVal;
q.offer(new Tuple(newRow, newCol, newVal));
}
} else {
if (dp[newRow][newCol][0] < newVal) {
dp[newRow][newCol][0] = newVal;
q.offer(new Tuple(newRow, newCol, newVal));
}
}
}
}
}
int ans = (int)(dp[n - 1][m - 1][0] % mod);
if (ans < 0)
ans = -1;
if (ans == -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0)
return 0;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here