1478. Maximum Number Of Events That Can Be Attended¶
Difficulty: Medium
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
1478. Maximum Number of Events That Can Be Attended
Medium
You are given an array of events where events[i] = [startDayi, endDayi]. Every event i starts at startDayi and ends at endDayi.
You can attend an event i at any day d where startTimei <= d <= endTimei. You can only attend one event at any time d.
Return the maximum number of events you can attend.
Example 1:
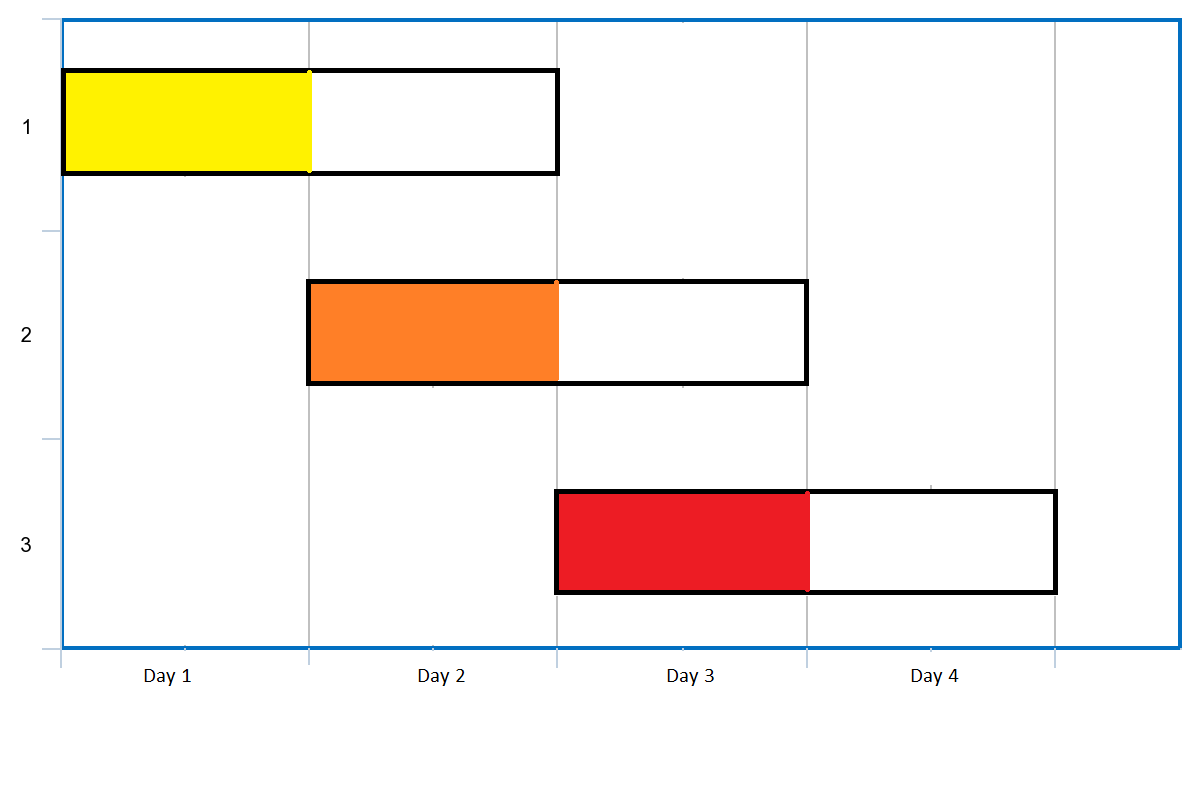
Input: events = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]] Output: 3 Explanation: You can attend all the three events. One way to attend them all is as shown. Attend the first event on day 1. Attend the second event on day 2. Attend the third event on day 3.
Example 2:
Input: events= [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,2]] Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= events.length <= 105events[i].length == 21 <= startDayi <= endDayi <= 105
Solution¶
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Solution {
static class Pair {
int start, end;
public Pair(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pair{" +
"start=" + start +
", end=" + end +
'}';
}
}
static class customSort implements Comparator<Pair> {
@Override
public int compare(Pair first, Pair second) {
int op1 = Integer.compare(first.start, second.start);
if (op1 != 0)
return op1;
return Integer.compare(first.end, second.end);
}
}
public int maxEvents(int[][] arr) {
int n = arr.length, m = arr[0].length;
ArrayList<Pair> events = new ArrayList<>();
for (int current[] : arr)
events.add(new Pair(current[0], current[1]));
Collections.sort(events, new customSort());
int currentIdx = 0, count = 0, currentDay = 1, lastDay = 0;
for (Pair e : events)
lastDay = Math.max(lastDay, e.end);
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
while (currentDay <= lastDay) {
while (currentIdx < n && events.get(currentIdx).start <= currentDay) {
pq.offer(events.get(currentIdx).end);
currentIdx++;
}
while (pq.size() > 0 && pq.peek() < currentDay)
pq.poll();
if (pq.size() > 0) {
count++;
pq.poll();
}
currentDay++;
}
return count;
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here