1387. Find Elements In A Contaminated Binary Tree¶
Difficulty: Medium
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
1387. Find Elements in a Contaminated Binary Tree
Medium
Given a binary tree with the following rules:
root.val == 0- For any
treeNode:- If
treeNode.valhas a valuexandtreeNode.left != null, thentreeNode.left.val == 2 * x + 1 - If
treeNode.valhas a valuexandtreeNode.right != null, thentreeNode.right.val == 2 * x + 2
- If
Now the binary tree is contaminated, which means all treeNode.val have been changed to -1.
Implement the FindElements class:
FindElements(TreeNode* root)Initializes the object with a contaminated binary tree and recovers it.bool find(int target)Returnstrueif thetargetvalue exists in the recovered binary tree.
Example 1:
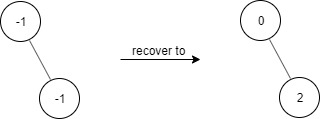
Input ["FindElements","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1]],[1],[2]] Output [null,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return False findElements.find(2); // return True
Example 2:
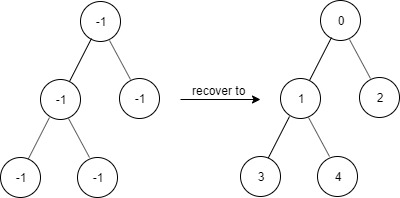
Input ["FindElements","find","find","find"] [[[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]],[1],[3],[5]] Output [null,true,true,false] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return True findElements.find(3); // return True findElements.find(5); // return False
Example 3:
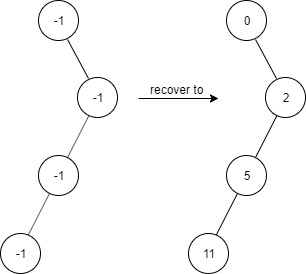
Input ["FindElements","find","find","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]],[2],[3],[4],[5]] Output [null,true,false,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(2); // return True findElements.find(3); // return False findElements.find(4); // return False findElements.find(5); // return True
Constraints:
TreeNode.val == -1- The height of the binary tree is less than or equal to
20 - The total number of nodes is between
[1, 104] - Total calls of
find()is between[1, 104] 0 <= target <= 106
Solution¶
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class FindElements {
private TreeNode new_root;
private HashSet<Integer> set;
public FindElements(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> q1 = new LinkedList<>();
new_root = new TreeNode(0);
set = new HashSet<>();
q.offer(new_root);
q1.offer(root);
while (q.size() > 0) {
int len = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode current = q.peek();
int val = q.peek().val;
set.add(val);
if (q1.peek().left != null) {
current.left = new TreeNode(val * 2 + 1);
q.offer(current.left);
q1.offer(q1.peek().left);
set.add(val * 2 + 1);
}
if (q1.peek().right != null) {
current.right = new TreeNode(val * 2 + 2);
q.offer(current.right);
q1.offer(q1.peek().right);
set.add(val * 2 + 2);
}
q.poll();
q1.poll();
}
}
}
public boolean find(int target) {
return set.contains(target);
}
}
/**
* Your FindElements object will be instantiated and called as such:
* FindElements obj = new FindElements(root);
* boolean param_1 = obj.find(target);
*/
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here