1342. Queens That Can Attack The King¶
Difficulty: Medium
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
1342. Queens That Can Attack the King
Medium
On a 0-indexed 8 x 8 chessboard, there can be multiple black queens and one white king.
You are given a 2D integer array queens where queens[i] = [xQueeni, yQueeni] represents the position of the ith black queen on the chessboard. You are also given an integer array king of length 2 where king = [xKing, yKing] represents the position of the white king.
Return the coordinates of the black queens that can directly attack the king. You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
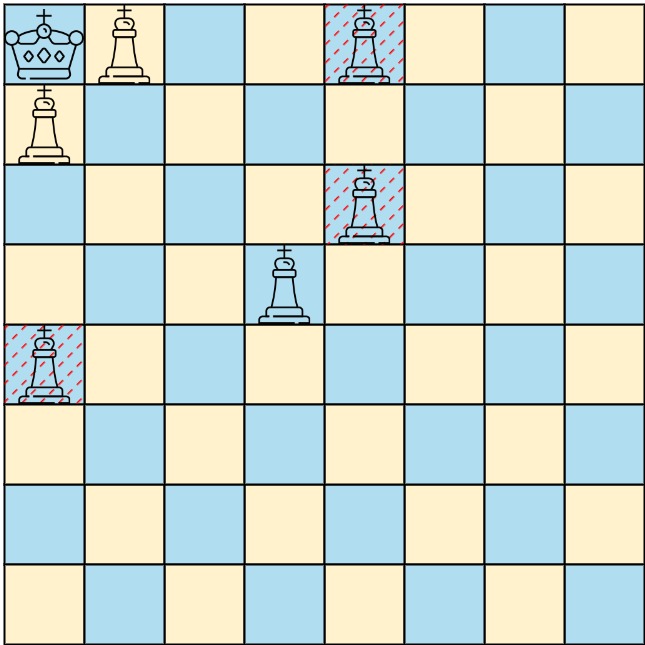
Input: queens = [[0,1],[1,0],[4,0],[0,4],[3,3],[2,4]], king = [0,0] Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[3,3]] Explanation: The diagram above shows the three queens that can directly attack the king and the three queens that cannot attack the king (i.e., marked with red dashes).
Example 2:
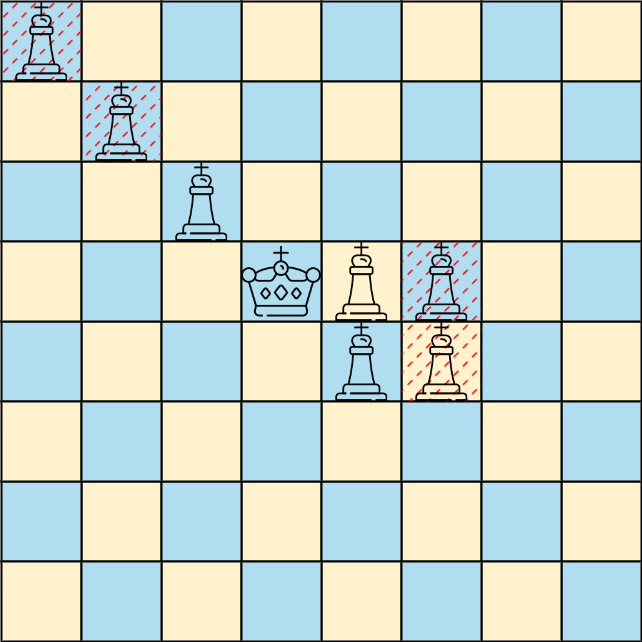
Input: queens = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[3,5],[4,4],[4,5]], king = [3,3] Output: [[2,2],[3,4],[4,4]] Explanation: The diagram above shows the three queens that can directly attack the king and the three queens that cannot attack the king (i.e., marked with red dashes).
Constraints:
1 <= queens.length < 64queens[i].length == king.length == 20 <= xQueeni, yQueeni, xKing, yKing < 8- All the given positions are unique.
Solution¶
class Solution {
static HashSet<Pair> set;
static class Pair {
int row, col;
public Pair(int row, int col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + row + " " + col + ")";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) return true;
if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;
Pair current = (Pair)(obj);
return current.row == row && current.col == col;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(row, col);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> queensAttacktheKing(int[][] queens, int[] king) {
int n = queens.length;
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
set = new HashSet<>();
for (int pos[] : queens) set.add(new Pair(pos[0] , pos[1]));
for (int pos[] : queens) {
if (can_attack(pos[0] , pos[1] , king[0] , king[1])) {
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
temp.add(pos[0]); temp.add(pos[1]);
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
}
return res;
}
static boolean can_attack(int x, int y , int rx, int ry) {
int n = 8, m = 8;
//Right
int cx = x, cy = y + 1;
while (cy < m) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cy++;
}
//Left
cx = x; cy = y - 1;
while (cy >= 0) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cy--;
}
//Down
cx = x + 1; cy = y;
while (cx < n) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cx++;
}
//Up
cx = x - 1; cy = y;
while (cx >= 0) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cx--;
}
//Right Upper Diagonal
cx = x - 1; cy = y + 1;
while (cx >= 0 && cy < m) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cx--; cy++;
}
//Left Upper Diagonal
cx = x - 1; cy = y - 1;
while (cx >= 0 && cy >= 0) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cx--; cy--;
}
//Lower Left Diagonal
cx = x + 1; cy = y - 1;
while (cx < n && cy >= 0) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cx++; cy--;
}
//Lower Right Diagonal
cx = x + 1; cy = y + 1;
while (cx < n && cy < m) {
if (set.contains(new Pair(cx , cy))) break;
if (cx == rx && cy == ry) return true;
cx++; cy++;
}
return false;
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here