1218. Lowest Common Ancestor Of Deepest Leaves¶
Difficulty: Medium
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
1218. Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, return the lowest common ancestor of its deepest leaves.
Recall that:
- The node of a binary tree is a leaf if and only if it has no children
- The depth of the root of the tree is
0. if the depth of a node isd, the depth of each of its children isd + 1. - The lowest common ancestor of a set
Sof nodes, is the nodeAwith the largest depth such that every node inSis in the subtree with rootA.
Example 1:
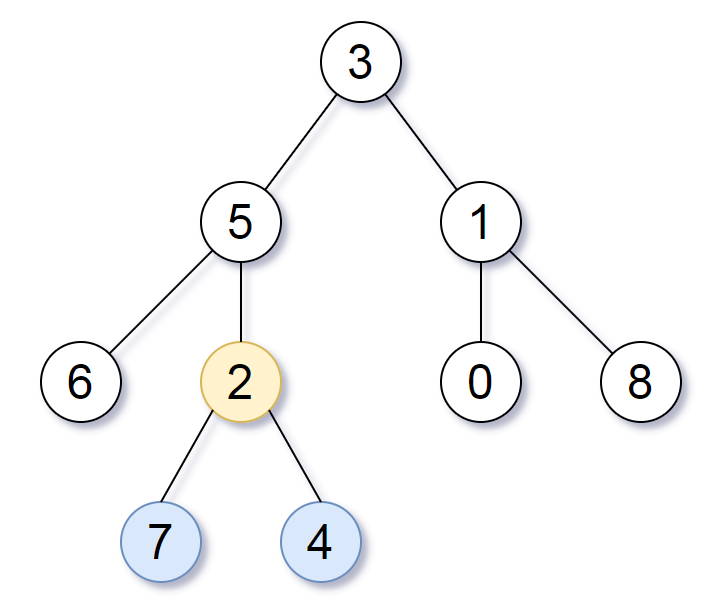
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] Output: [2,7,4] Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram. The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest leaf-nodes of the tree. Note that nodes 6, 0, and 8 are also leaf nodes, but the depth of them is 2, but the depth of nodes 7 and 4 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1] Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree, and it's the lca of itself.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2] Output: [2] Explanation: The deepest leaf node in the tree is 2, the lca of one node is itself.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
Note: This question is the same as 865: https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/
Solution¶
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
static class Pair {
TreeNode node;
int depth;
public Pair(TreeNode node, int depth) {
this.node = node;
this.depth = depth;
}
}
public TreeNode lcaDeepestLeaves(TreeNode root) {
int depth[] = new int[1000 + 6];
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i <= 1000 + 5; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Pair(root, 0));
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(q.peek().node.left != null) {
q.offer(new Pair(q.peek().node.left , q.peek().depth + 1));
int u = q.peek().node.val;
int v = q.peek().node.left.val;
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
if(q.peek().node.right != null) {
q.offer(new Pair(q.peek().node.right,q.peek().depth + 1));
int u = q.peek().node.val;
int v = q.peek().node.right.val;
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
depth[q.peek().node.val] = q.peek().depth;
q.poll();
}
}
int maxi = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= 1000; i++) maxi = Math.max(maxi, depth[i]);
ArrayList<Integer> deepest_node = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i <= 1000; i++) {
if(depth[i] == maxi) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
deepest_node.add(i);
}
}
int dp[][] = new int[1000 + 5][18];
dfs(root.val,0,adj,dp);
int ans = deepest_node.get(0);
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < deepest_node.size(); i++) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < deepest_node.size(); j++) {
int a = deepest_node.get(i);
int b = deepest_node.get(j);
int lca = lca(a, b, dp,depth);
if(depth[lca] < min) {
min = depth[lca];
ans = lca;
}
}
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return root;
return find(root, ans);
}
private TreeNode find(TreeNode root , int res) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(q.peek().val == res) return q.peek();
if(q.peek().left != null) q.offer(q.peek().left);
if(q.peek().right != null) q.offer(q.peek().right);
q.poll();
}
}
return null;
}
private void dfs(int u , int par, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj ,int dp[][]) {
dp[u][0] = par;
for(int i = 1; i <= 17; i++) dp[u][i] = dp[dp[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
for(int v : adj.get(u)) {
if(v != par) dfs(v, u, adj, dp);
}
}
private int lca(int a , int b , int dp[][],int depth[]) {
if(depth[a] > depth[b]) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int diff = depth[b] - depth[a];
b = find_kth_parent(b, diff, dp);
if(a == b) return a;
for(int i = 17; i >= 0; i--) {
if(dp[a][i] != dp[b][i]) {
a = dp[a][i];
b = dp[b][i];
}
}
return dp[a][0];
}
private int find_kth_parent(int u , int k , int dp[][]) {
int count = 0;
while(k != 0) {
if(k % 2 == 1) u = dp[u][count];
count++;
k = k >> 1;
}
return u;
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here