407. Trapping Rain Water Ii¶
Difficulty: Hard
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
407. Trapping Rain Water II
Hard
Given an m x n integer matrix heightMap representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, return the volume of water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
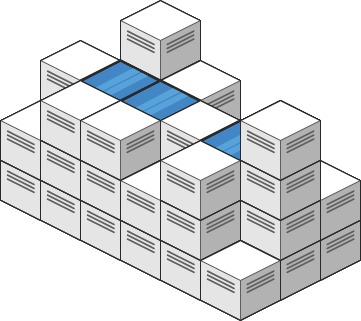
Input: heightMap = [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] Output: 4 Explanation: After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. We have two small ponds 1 and 3 units trapped. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
Example 2:
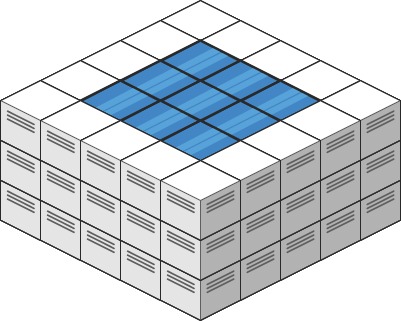
Input: heightMap = [[3,3,3,3,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,2,1,2,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,3,3,3,3]] Output: 10
Constraints:
m == heightMap.lengthn == heightMap[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 2 * 104
Solution¶
class Solution {
static class Tuple {
int row, col, cost;
public Tuple(int row, int col, int cost) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + row + " " + col + " " + cost + ")";
}
}
static class customSort implements Comparator<Tuple> {
@Override
public int compare(Tuple first, Tuple second) {
return Integer.compare(first.cost, second.cost);
}
}
public int trapRainWater(int[][] arr) {
int n = arr.length, m = arr[0].length;
int vis[][] = new int[n][m];
PriorityQueue<Tuple> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new customSort());
int dir[][] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pq.offer(new Tuple(i, 0, arr[i][0]));
pq.offer(new Tuple(i, m - 1, arr[i][m - 1]));
vis[i][0] = 1;
vis[i][m - 1] = 1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
pq.offer(new Tuple(0, j, arr[0][j]));
pq.offer(new Tuple(n - 1, j, arr[n - 1][j]));
vis[0][j] = 1;
vis[n - 1][j] = 1;
}
int res = 0;
while (pq.size() > 0) {
int currRow = pq.peek().row, currCol = pq.peek().col, currCost = pq.peek().cost;
pq.poll();
for (int dire[] : dir) {
int newRow = currRow + dire[0], newCol = currCol + dire[1];
if (newRow < n && newRow >= 0 && newCol < m && newCol >= 0 && vis[newRow][newCol] == 0) {
vis[newRow][newCol] = 1;
res += Math.max(0, currCost - arr[newRow][newCol]);
pq.offer(new Tuple(newRow, newCol, Math.max(arr[newRow][newCol], currCost)));
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here