99. Recover Binary Search Tree¶
Difficulty: Medium
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
99. Recover Binary Search Tree
Medium
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where the values of exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example 1:
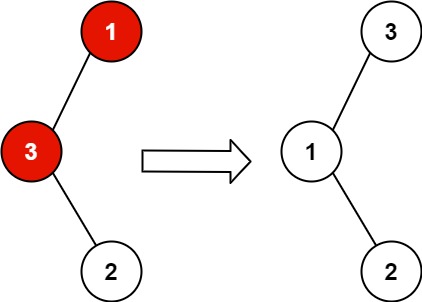
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2] Output: [3,1,null,null,2] Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:
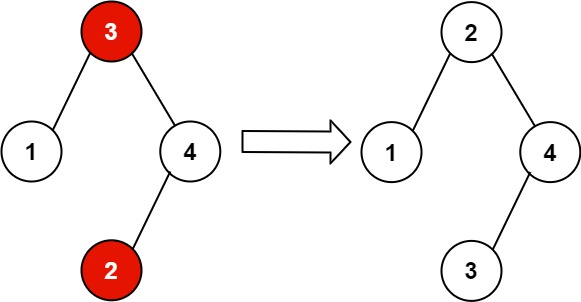
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3] Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Follow up: A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight-forward. Could you devise a constant O(1) space solution?
Solution¶
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
Definition for a binary tree node.
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
private ArrayList<Integer> inorderList;
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
inorderList = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root);
int a = -1, b = -1;
ArrayList<Integer> sortedList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorderList.size(); i++)
sortedList.add(inorderList.get(i));
Collections.sort(sortedList);
for (int i = 0; i < sortedList.size(); i++) {
if (sortedList.get(i) != inorderList.get(i)) {
if (a == -1)
a = sortedList.get(i);
else
b = sortedList.get(i);
}
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (q.size() > 0) {
int len = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (q.peek().left != null)
q.offer(q.peek().left);
if (q.peek().right != null)
q.offer(q.peek().right);
if (q.peek().val == a)
q.peek().val = b;
else if (q.peek().val == b)
q.peek().val = a;
q.poll();
}
}
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left);
inorderList.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right);
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here