25. Reverse Nodes In K Group¶
Difficulty: Hard
LeetCode Problem View on GitHub
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Hard
Given the head of a linked list, reverse the nodes of the list k at a time, and return the modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
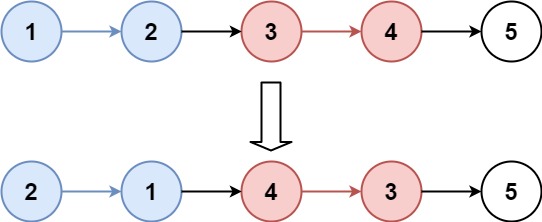
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:
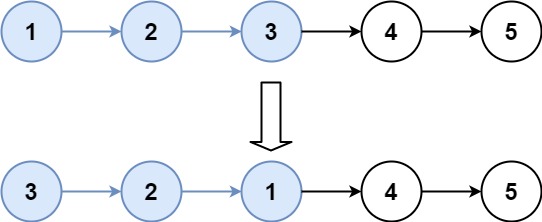
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Follow-up: Can you solve the problem in O(1) extra memory space?
Solution¶
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
res.add(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (left < res.size()) {
int current_pointer = k;
ArrayList<Integer> temp_nodes = new ArrayList<>();
while (right < res.size() && current_pointer > 0) {
current_pointer--;
temp_nodes.add(res.get(right++));
}
if (temp_nodes.size() == k) Collections.reverse(temp_nodes);
for (int ele : temp_nodes) nodes.add(ele);
left = right;
}
Collections.reverse(nodes);
ListNode res_node = new ListNode(nodes.get(0));
for (int i = 1; i < nodes.size(); i++) {
res_node = insert(res_node, nodes.get(i));
}
return res_node;
}
private ListNode insert(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode to_insert = new ListNode(val);
to_insert.next = head;
head = to_insert;
return head;
}
}
Complexity Analysis¶
- Time Complexity:
O(?) - Space Complexity:
O(?)
Approach¶
Detailed explanation of the approach will be added here